Introduction
Cataracts remain the leading cause of blindness globally, affecting millions, particularly in developing countries where access to timely and effective treatment can be limited. Traditional cataract surgery methods, while effective, often come with longer recovery times and higher complication rates. Enter phacoemulsification – a modern, minimally invasive technique that is transforming the landscape of cataract surgery, especially in regions that need it most. This blog explores how phacoemulsification is revolutionizing eye care in developing countries and compares it with traditional cataract surgery methods.
Understanding Phacoemulsification Cataract Surgery
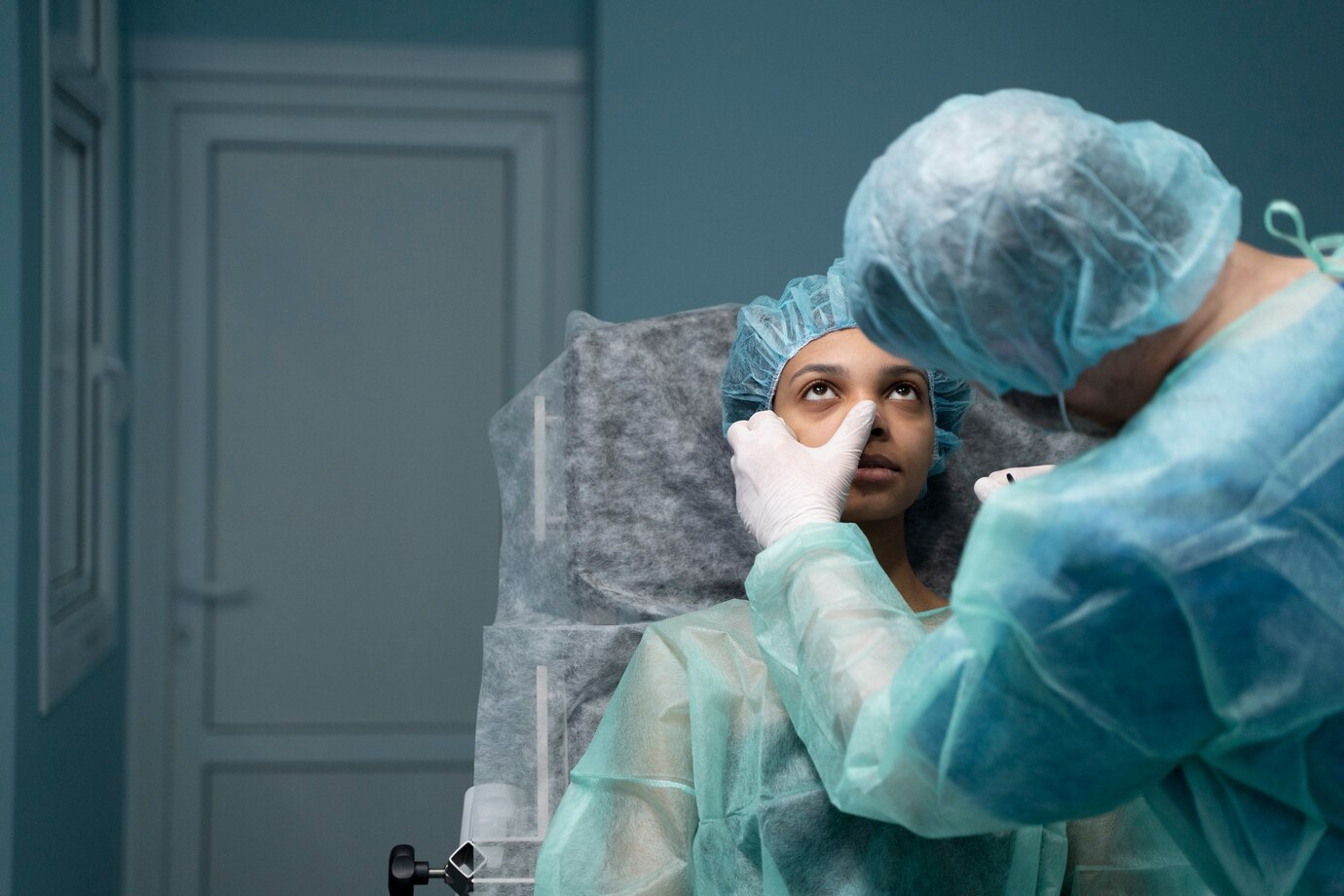
Phacoemulsification, commonly referred to as “phaco,” involves using ultrasonic energy to emulsify the eye’s natural lens, which has become cloudy due to cataracts. This emulsified lens is then aspirated or sucked out and replaced with a clear artificial intraocular lens (IOL). The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia and is minimally invasive, requiring only a small incision.
Key Benefits of Phacoemulsification:
- Minimally Invasive: Requires a small incision, usually less than 3mm.
- Rapid Recovery: Shorter healing time, with many patients regaining good vision within a day or two.
- High Precision: Advanced technology allows for more precise removal of the cataract and better visual outcomes.
- Less Postoperative Complication: Reduced risk of infection and less induced astigmatism compared to traditional methods.
Phacoemulsification vs. Traditional Cataract Surgery: What’s the Difference?
Traditional cataract surgery, often referred to as extracapsular cataract extraction (ECCE), involves making a larger incision in the eye to remove the cloudy lens in one piece. This method, while still in use and effective, typically requires a longer recovery period and carries a higher risk of postoperative complications compared to phacoemulsification.
Comparative Points:
1. Surgical Incision Size:
- Phacoemulsification: Involves a small incision (1.8-3mm), which promotes faster healing and minimal scarring.
- Traditional Surgery: Requires a larger incision (around 10-12mm), leading to a longer healing process and potentially more postoperative discomfort.
2. Lens Removal Technique:
- Phacoemulsification: Uses ultrasonic energy to break up the lens into smaller pieces that are then aspirated out.
- Traditional Surgery: Removes the entire lens in one piece, necessitating a larger incision.
3. Recovery Time:
- Phacoemulsification: Typically offers a quicker recovery, with most patients resuming normal activities within a few days.
- Traditional Surgery: Recovery can take several weeks, with more stringent postoperative care requirements.
4. Visual Outcomes:
- Phacoemulsification: Generally results in more precise visual correction and less induced astigmatism.
- Traditional Surgery: Effective but with a higher likelihood of postoperative visual disturbances due to the larger incision and sutures required.
5. Postoperative Care:
- Phacoemulsification: Involves fewer postoperative restrictions and a lower risk of infection.
- Traditional Surgery: Requires more intensive postoperative care and has a higher risk of infection and other complications due to the larger incision.
How Phacoemulsification is Transforming Eye Care in Developing Countries
Accessibility and Affordability
In developing countries, where healthcare resources are often limited, the adoption of phacoemulsification has been a game-changer. Initially perceived as costly, the procedure has become more affordable and accessible through partnerships with non-profit organizations, government programs, and global health initiatives. Mobile surgical units and community outreach programs have brought this advanced surgery to remote areas, significantly improving access to care.
Efficiency and Scalability
Phacoemulsification’s efficiency is another critical factor in its widespread adoption in developing countries. The procedure’s shorter operating time and rapid patient turnover mean that more surgeries can be performed in a day compared to traditional methods. This efficiency is crucial in regions with a high prevalence of cataracts and long waiting lists for surgery.
Improved Surgical Outcomes
With phacoemulsification, patients experience quicker visual rehabilitation and fewer complications. This is particularly beneficial in developing countries, where postoperative follow-up can be challenging due to logistical constraints. The reduced need for postoperative care and monitoring allows healthcare providers to focus on treating more patients.
Training and Skill Development
The spread of phacoemulsification has also driven improvements in surgical training and capacity building in developing countries. Local ophthalmologists are receiving training in this advanced technique, enhancing their skills and increasing the overall quality of eye care in their communities. This knowledge transfer is crucial for sustaining the benefits of phacoemulsification and empowering local healthcare systems.
Conclusion
Phacoemulsification has revolutionized cataract surgery, providing a safer, more efficient, and more accessible solution for millions suffering from vision impairment due to cataracts. Its adoption in developing countries marks a significant step forward in global eye care, offering hope and restored vision to those who need it most.
As healthcare systems continue to evolve and integrate advanced technologies like phacoemulsification, the outlook for cataract patients in developing regions becomes increasingly bright. This modern technique not only restores sight but also enhances the quality of life, enabling individuals to lead more productive and fulfilling lives.

Leave A Comment